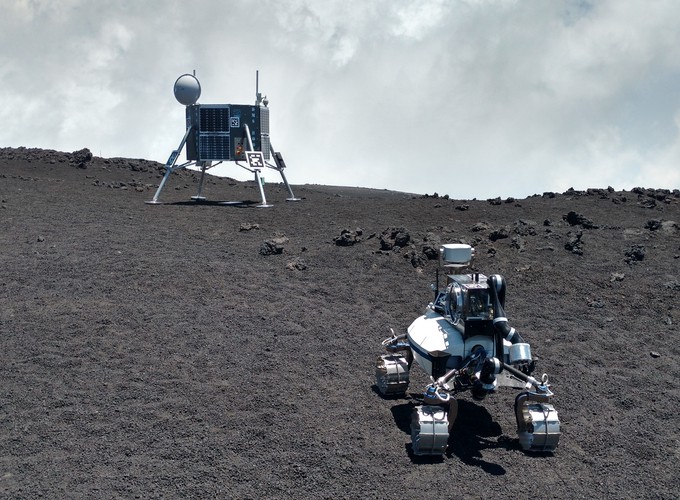
For the Demonstration Mission Space a dedicated scenario was chosen by the ROBEX lunar scientists. The scenario describes the installation of an active seismic network (ASN) on the Moon’s surface. The main focus is the measurement of the internal structure and the composition of the upper layer, the lunar regolith. Other questions are the existence and composition of a central core of the Moon and if there is any seismic activity. The seismometers are planned to be transported by a rover and put down on surface by means of a robotic arm.
The analogue mission on the Mt. Etna basically consisted of two individual experiments: First, our rover mapped the lander site, deployed the seismic instrument, waited until one measurement cycle was done, took it up again and repeated the measurement on several points of interest. In the second experiment, the rover had to set up a seismic network consisting of four instruments that had to be arranged at three corner points and the center point of an equilateral triangle of about 100 m. Both scenarios required the robot to be equipped with highly robust navigation, perception and manipulation capabilities in order to place the instruments carefully and precisely onto the ground. Our robot was able to perform these tasks fully autonomously.
My responsibilities: Autonomous Task Control, System Architecture, Task Execution Logging and Profiling, Semantic World Modeling